Key energy standards across Europe and North America for optimizing efficiency and demand response

As the world grapples with escalating energy demands and the pressing need for sustainability, the role of demand response (DR) and energy efficiency (EE) has never been more critical. Energy standards in these areas are vital as they ensure a cohesive approach to managing energy consumption, enhancing efficiency, and integrating renewable energy sources. They provide a framework for developing, implementing, and maintaining technologies that contribute to a more resilient and sustainable energy system.
Standards in the energy industry, such as OpenADR, Energy Star, and various regional directives, offer a blueprint for utilities, manufacturers, and consumers to follow. These standards define the technical specifications, performance criteria, and compliance requirements necessary to achieve desired energy outcomes. However, the implementation of these energy standards comes with its own set of advantages and challenges.
Pros and cons of energy standards in the energy industry
Implementing energy standards brings both significant benefits and challenges, impacting various stakeholders in the energy sector. While these standards ensure consistency, reliability, and improved energy efficiency, they also come with certain drawbacks that need to be considered. Understanding the pros and cons of energy standards is essential for stakeholders aiming to navigate the complexities of energy management effectively.
Pros:
- Consistency and Reliability: Energy standards ensure that energy systems and devices operate reliably and consistently, facilitating seamless integration and interoperability across different regions and technologies.
- Improved Energy Efficiency: By setting benchmarks for energy performance, energy standards drive innovation and encourage the development of more efficient technologies and practices.
- Market Confidence: Energy standards provide consumers and businesses with confidence in the products and services they use, knowing they meet established quality and efficiency criteria.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to energy standards helps organizations comply with national and international regulations, avoiding penalties and enhancing their reputation.
- Environmental Benefits: Energy standards promote sustainable practices and the adoption of renewable energy sources, contributing to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions.
Cons:
- Implementation Costs: Complying with energy standards can entail significant costs for businesses, including investments in new technologies, training, and compliance monitoring.
- Complexity: Navigating the myriad of energy standards and ensuring compliance across different regions can be complex and time-consuming for multinational organizations.
- Inflexibility: Some energy standards may be rigid, making it challenging for businesses to adapt quickly to new technologies or market demands.
- Variation Across Regions: Differences in energy standards between regions can create barriers to international trade and complicate the global supply chain.
How energy standards work in the energy industry
Energy standards in the energy industry are developed through collaborative efforts involving government agencies, industry stakeholders, and technical experts. They undergo rigorous testing, validation, and review processes to ensure they are robust and applicable to real-world scenarios. Once established, these energy standards are implemented through regulations, certifications, and compliance programs.
One of the earliest and most influential energy standards in the energy sector is the Energy Star program, launched in 1992 by the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Energy Star was the first standard to set comprehensive criteria for energy efficiency across a wide range of products, including appliances, electronics, and buildings. It has since become a global symbol of energy efficiency, widely recognized and adopted by manufacturers and consumers worldwide.
Demand response and energy efficiency standards in the US
1. OpenADR (Open Automated Demand Response)
OpenADR is a crucial energy standard developed in the US to facilitate the communication of demand response signals between utilities and customers. It automates the DR process, making it easier for both utilities and customers to participate in DR programs.
Implementation and Requirements: OpenADR allows for standardized communication protocols that enable automated, reliable, and secure two-way information exchange between utilities and customers. This energy standard supports various DR programs, including peak load management and real-time pricing.
Mandatory Adoption: States like California have mandated the use of OpenADR for utilities and large commercial buildings to manage peak demand and integrate renewable energy sources efficiently.
The adoption of OpenADR in California has led to significant load reductions during peak demand periods, showcasing the effectiveness of automated DR systems.
2. Energy Star
Energy Star is a voluntary program run by the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) that certifies energy-efficient products. It is widely recognized and used as a benchmark for energy efficiency in various sectors.
Office Equipment: The US EPA’s Energy Star program certifies a wide range of office equipment, ensuring that products meet specific energy efficiency criteria. Certified products typically use 25-30% less energy than their non-certified counterparts.
Impact and Compliance: Many states and municipalities have adopted Energy Star energy standards as part of their energy efficiency regulations. For instance, New York City requires large commercial buildings to meet Energy Star benchmarks as part of its Local Law 97.
3. IEEE Standards
IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) has developed several standards that are essential for the integration and interoperability of demand response and energy efficiency technologies.
- IEEE 2030.5 (Smart Energy Profile 2.0): This standard provides guidelines for smart grid communications, enhancing the communication between various energy devices and the grid. It supports secure, reliable, and efficient two-way communication, crucial for advanced energy management and demand response systems.
- IIEEE 1547: This standard specifies the criteria for interconnection and interoperability of distributed energy resources (DERs) with the grid. It ensures that DERs, such as solar panels and wind turbines, can safely and efficiently integrate with the broader energy system, promoting the use of renewable energy sources and enhancing grid stability.
By implementing IEEE standards, utilities and technology providers can ensure that their systems are compatible with a wide range of devices and platforms, fostering innovation and improving the overall efficiency and reliability of the energy grid.
Demand response and energy efficiency standards in Europe
Europe has been proactive in developing and implementing energy standards to promote energy efficiency and demand response. Here are some key energy standards across different countries:
- United Kingdom
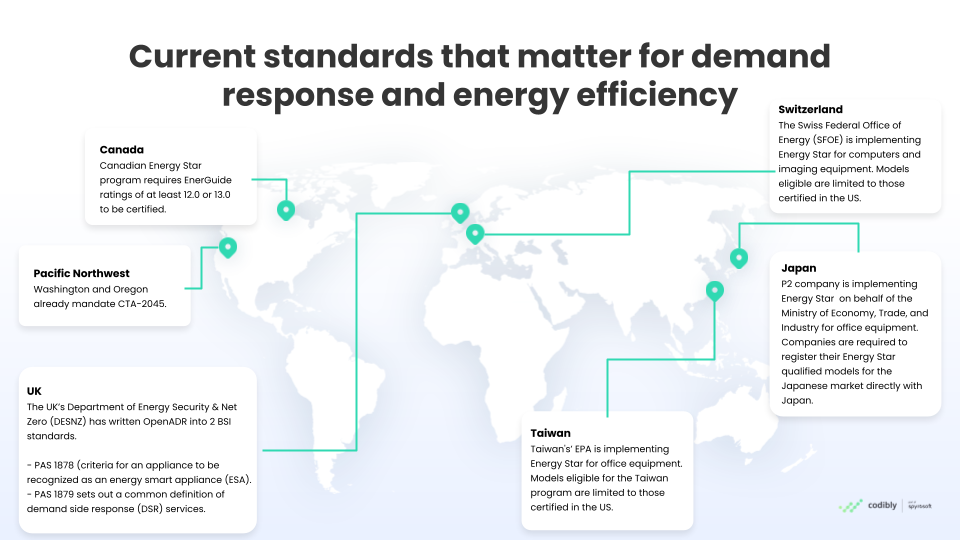
The UK has developed PAS 1878 and PAS 1879, crucial for its DR and EE landscape. Developed by the UK’s Department of Energy Security & Net Zero (DESNZ), these energy standards are vital.
- PAS 1878: Specifies criteria for recognizing an appliance as an energy smart appliance (ESA). This includes requirements for interoperability, security, and user functionality.
- PAS 1879: Provides a common definition of demand side response (DSR) services, outlining the types of DSR and the roles of different market participants.
Legal Requirements: The UK government has integrated these energy standards into its national regulations, making compliance mandatory for certain categories of appliances and services.
The UK’s Smart Energy Code (SEC) incorporates PAS energy standards to ensure smart meters and appliances can participate in DR programs, leading to more effective energy management and reduced peak demand.
- Switzerland
Switzerland’s commitment to energy efficiency is exemplified by its adoption of the Energy Star program for Computers and Imaging Equipment, managed by the Federal Office of Energy (SFOE). This initiative ensures that only the most energy-efficient products, certified in the US, are available in the market.
Energy Star for Computers and Imaging Equipment: Switzerland’s Federal Office of Energy (SFOE) implements the Energy Star program specifically for computers and imaging equipment. Models eligible for certification are limited to those certified in the US, ensuring high standards of energy efficiency.
Impact: This adoption ensures that only the most energy-efficient products are available in the market, promoting significant energy savings across the IT sector.
- Germany
Germany, being a leader in renewable energy adoption, has developed robust energy standards to support energy efficiency and demand response.
DIN EN 15232: This energy standard focuses on the energy performance of buildings, specifying the impact of building automation and control systems on energy efficiency.
Mandatory Compliance: Buildings in Germany must meet this energy standard to achieve certain energy efficiency certifications, impacting both new constructions and renovations.
BDEW Smart Grid Traffic Light Concept: This framework helps manage the distribution grid, ensuring stability and integrating renewable energy sources effectively.
This concept is widely used in Germany to balance supply and demand in the grid, particularly during periods of high renewable energy production.
- France
France has implemented several initiatives to support demand response and energy efficiency, aligning with European Union directives.
RT 2012 and RT 2020: These regulations set stringent energy performance requirements for new buildings, promoting high energy efficiency standards.
Mandatory Standards: Compliance with these energy standards is required for all new buildings, significantly impacting the construction industry and promoting sustainable building practices.
NEBEF (Notification d’Échanges de Blocs d’Efficacité Énergétique): A demand response mechanism that allows consumers to participate in the energy market by offering their flexibility services.
Large commercial consumers in France have successfully participated in NEBEF, contributing to grid stability and earning incentives for their flexibility.
- Poland
Poland is steadily advancing in the realm of demand response and energy efficiency.
National Fund for Environmental Protection and Water Management (Narodowy Fundusz Ochrony Środowiska i Gospodarki Wodnej): This body supports various energy efficiency projects, including the implementation of demand response programs.
Funding and Support: NFEPWM provides grants and financial incentives for projects that enhance energy efficiency and integrate DR technologies.
Energy Efficiency Act: This legislation mandates energy audits and sets energy savings targets for large enterprises, encouraging the adoption of energy-efficient practices.
Compliance: Large enterprises are required to conduct regular energy audits and implement recommended measures to achieve specified energy savings targets.
Global implementation and trends
Energy standards play a critical role in shaping energy efficiency and demand response practices worldwide. Countries outside of Europe and the US have also adopted various energy standards to promote sustainability and reduce energy consumption.
- Canada
The Canadian Energy Star Program sets rigorous energy efficiency benchmarks, requiring EnerGuide ratings of at least 12.0 or 13.0 for certification. This ensures that products meet stringent energy efficiency standards. By establishing these high benchmarks, Canada encourages the adoption of energy-efficient products and practices across various sectors, from residential appliances to commercial equipment. This program not only reduces energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions but also helps consumers save on energy bills. The widespread recognition of the Energy Star label in Canada supports the transition towards a more sustainable and energy-efficient future.
- Japan
In Japan, the Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry (METI) oversees the implementation of the Energy Star program for office equipment. Companies are required to register their Energy Star qualified models directly with Japan. This ensures that only certified energy-efficient models are available in the Japanese market. The stringent energy-saving standards help Japan achieve significant energy savings and reduce its carbon footprint. By aligning with international energy efficiency standards, Japan promotes the development and use of high-efficiency technologies, supporting its national goals for energy conservation and environmental protection.
- Taiwan
Taiwan’s Environmental Protection Administration (EPA) implements the Energy Star program for office equipment, aligning with US energy standards. Models eligible for the Taiwan program are limited to those certified in the US, ensuring that they meet a high standard of energy efficiency. This alignment helps Taiwan maintain high energy efficiency across its IT and office equipment sectors. By adopting these stringent standards, Taiwan reduces energy consumption and enhances the sustainability of its technology infrastructure. The Energy Star program in Taiwan also promotes innovation and competitiveness among manufacturers, driving the market towards more efficient and eco-friendly products.
Demand response and energy standards are a key
The adoption and implementation of demand response and energy efficiency standards vary across regions but share a common goal of promoting sustainable energy use. For energy market players, understanding these energy standards is crucial for ensuring compliance and leveraging opportunities in different markets. Whether it’s OpenADR in the US, PAS standards in the UK, or Energy Star programs globally, staying informed about these energy standards can significantly enhance energy management strategies and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Codibly stands ready to assist clients in navigating these energy standards, offering expertise and solutions that align with the latest regulations and best practices in demand response and energy efficiency. By leveraging Codibly’s insights and solutions, clients can optimize their energy use, reduce costs, and contribute to a greener planet.
Interested in learning more or need help with implementing energy efficiency standrads?
Contact Codibly today to explore tailored energy management solutions for your business.
contact us
Need expert guidance on your next energy project?
Reach out to us and discover how Codibly can offer tailored solutions to drive your business.